Hormone Imbalance During Puberty in Adolescence and Gynecomastia: Causes and Solutions

15 Min Read:
Hormonal imbalance during puberty in adolescents and gynecomastia are closely related, where boys develop breast tissue. Pubertal gynecomastia is a common occurrence during puberty in boys and often resolves spontaneously within one to two years. This condition often causes distress, but understanding its causes and treatments can help manage it. This article will explain why this happens and how to address it.
Key Takeaways
- Gynecomastia in adolescent boys is primarily caused by hormonal imbalances, particularly the conversion of testosterone into estrogen, leading to breast tissue growth, which often resolves on its own but requires accurate diagnosis to rule out other conditions.
- Effective management of gynecomastia includes both monitoring and non-surgical approaches, such as lifestyle changes, as well as medical treatments like hormone therapy and, in severe cases, surgical interventions.
- Gynecomastia can have significant psychological impacts, necessitating psychological support through counseling and support groups to address associated mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
Hormonal Changes During Puberty in Boys
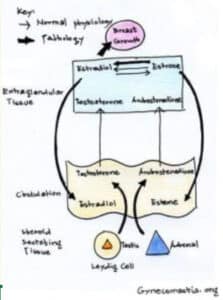
The onset of puberty for boys, typically occurring between 9 and 14 years of age, initiates a host of physical transformations. These include rapid growth periods, the emergence of body hair, and voice deepening due to laryngeal changes. The catalyst behind these developments are shifts in hormone levels, most notably testosterone and hormones estrogen. Estrogen plays a crucial role in the development of gynecomastia, as an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen can lead to the growth of breast tissue.
The endocrine system regulates these hormonal changes.
During this pubertal stage, testosterone governs the formation of distinctly male traits. It plays a crucial role by stimulating growth in:
- Testicles
- Penis
- Triggering sperm production processes
- Prompting other secondary sexual characteristics
Despite its pivotal function in developing male features during puberty, it is significant because it can be metabolized into hormones like estrogen through aromatase action, which may elevate estrogen levels.
This hormonal imbalance sometimes results in breast tissue development within one or both breasts—a condition termed gynecomastia—characterized by unilateral or bilateral enlargement that could exhibit asymmetry with accompanying sensitivity or detectable nodules/fatty deposits under the nipple area. While self-resolving after three years from onset during adolescence as “pubertal gynecomastia,” discerning whether such symptoms are indicative instead of breast cancer remains critical for affected youths.
Understanding how increased receptivity to estrogen potentially exacerbates conditions requires an intricate exploration into how both testosterone’s primary functions interact throughout developmental stages alongside higher sensitivity to estrogens’ influence during maturation events.
Testosterone and Estrogen Dynamics
During puberty, testosterone production in the male body is essential for the formation of male sexual characteristics. In boys, both testosterone and estrogen—the latter being primarily associated with females—play a role in their sexual maturation. The enzyme known as aromatase can transform testosterone into estrogen. An excess of this activity may cause gynecomastia if hormonal balances are disrupted.
In boys, one main contributor to gynecomastia is the disproportion between testosterone and estrogen. If there’s an increase in estrogen compared to testosterone, it could lead to an enlargement of breast tissue. This fluctuation in hormone levels during puberty is often natural, and understanding this mechanism becomes crucial when addressing how to alleviate or control gynecomastia.
Sensitivity to Estrogen
Some boys may have an augmented sensitivity to estrogen, aside from hormonal imbalances, which can escalate the likelihood of gynecomastia. This increased sensitivity indicates that typical levels of estrogen could prompt more significant growth in breast tissue. Increased sensitivity to estrogen may be due to more estrogen receptors.
Due to this greater responsiveness to estrogen, individuals could experience moderate to severe breast enlargement, with accompanying symptoms like soreness and discomfort. In certain situations, this may evolve into persistent breast enlargement that doesn’t subside without additional medical intervention. Understanding each individual’s sensitivity to estrogen is crucial in tailoring appropriate treatment plans and support measures.
Causes of Gynecomastia in Adolescence
Several elements contribute to the development of gynecomastia in adolescents, including hormonal shifts related to puberty, exposure to certain medications and substances, as well as potential underlying medical or genetic issues. Each component plays a distinct role in how this condition manifests and continues over time.
It is important to note that male breast cancer, although rare, should be distinguished from gynecomastia. Male breast cancer has a low prevalence compared to other cancers, but recognizing its risk factors and understanding its relationship with gynecomastia is crucial in healthcare settings. It is rare to see in an adolescent male, and Dr. Delgado has never seen breast cancer in this age group.
The fluctuations of hormones typical during an adolescent boy’s puberty are often influenced by the adrenal glands, which are the primary factor leading to gynecomastia. These normal hormonal changes can create temporary imbalances, which could increase breast tissue. Hormonal therapy can sometimes be used to manage gynecomastia caused by these hormonal imbalances.
Various drugs, whether for recreational use or prescribed medications—including substances like marijuana and anabolic steroids—are known contributors to gynecomastia onset. As such, these agents could unintendedly trigger side effects. Consulting with a health professional is essential when initiating any new medication regime.
Certain ailments, along with inherited traits, also play their part in fostering gynecomastia. Among the conditions capable of inducing this disorder, one finds:
- Diseases affecting liver or kidneys
- Disruptions within hormone levels
- Excessive weight gain (obesity)
Anti-androgen drugs often used for prostate cancer treatment, performance-enhancing anabolic steroids frequently abused by athletes and bodybuilders alike, as well as select types of antidepressants, have all been associated with an increased risk for developing breast cancer.
Genetic irregularities could theoretically contribute, although they’re considered uncommon instances can’t be entirely dismissed. Dr. Delgado has certainly seen pubertal gynecomastia run in families.
Natural Hormone Fluctuations
During puberty, hormonal regulation can lead to an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone. This imbalance is mainly driven by elevated levels of estrogen compared to testosterone, resulting in the formation of breast tissue. Such hormone fluctuations may prompt some individuals to develop gynecomastia, or even severe gynecomastia, in more pronounced instances.
Speaking, most cases of gynecomastia that arise from these natural changes in hormones tend to resolve spontaneously within several months up to a few years. It’s crucial to be aware of how long the condition lasts, so as not only to understand, but also manage it properly when necessary.
Medication and Substance Influence
Various drugs and substances have a significant effect on the occurrence of gynecomastia. Notable triggers include:
- Muscle-enhancing anabolic steroids
- Illicit substances such as marijuana, amphetamines, heroin, and alcohol
- Herbal extracts like those found in tea tree or lavender oils
Some substances act as endocrine disruptors, which can lead to gynecomastia.
Being aware of these risk factors is crucial for anyone concerned about developing gynecomastia, and should warrant discussion with a medical professional.
To reduce the likelihood of experiencing gynecomastia, it’s advised to consult with a healthcare practitioner before initiating any new drug regimen, while steering clear of known contributing agents. Proactive awareness and management are key to preventing the condition from arising.
Diagnosing Gynecomastia in Adolescents
The process of diagnosing gynecomastia in adolescents begins with a detailed physical examination and the collection of medical history. This is an essential step to distinguish between gynecomastia and other conditions, as well as evaluating how much breast tissue has developed. Specific diagnostic criteria are used to differentiate gynecomastia from other conditions.
Diagnostic imaging techniques like ultrasound or mammography might be conducted. These procedures are valuable for analyzing the composition of the breast tissue and eliminating other potential causes for increased breast size.
Adopting this comprehensive method ensures a precise diagnosis, which allows healthcare providers to craft tailored treatment plans specific to each adolescent’s requirements.
Physical Examination
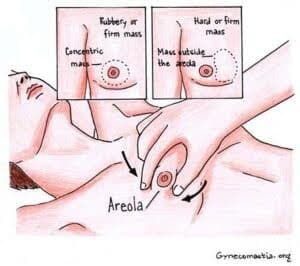
Plastic surgeons conduct a clinical evaluation of the palpable breast tissue for any lumps, alterations in skin appearance, and sensitivity during a physical examination. This process is crucial to distinguish between gynecomastia—which involves glandular tissue—and pseudogynecomastia—marked by fat accumulation.
In conducting the physical examination, practitioners scrutinize and feel the breasts to assess the dimensions and consistency of the tissue. Determining whether genuine gynecomastia exists through this method is imperative for devising additional diagnostic strategies when needed.
Blood Tests and Hormonal Evaluation
To diagnose gynecomastia accurately, it is important to conduct blood tests that can assess the hormonal profile and pinpoint any imbalances. These evaluations measure the serum levels of several hormones, such as:
- LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
- FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone)
- Testosterone
- Estradiol
To these assessments, a detailed hormonal study may also include checks for prolactin and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate.
For a complete picture, it’s important that all possible hormonal sources be considered—including those emanating from the pituitary gland—ensuring that no underlying cause is overlooked during this extensive diagnostic process.
Imaging Studies
During the diagnostic evaluation of gynecomastia, imaging techniques such as ultrasound and mammography play a crucial role. These methods become especially valuable when a breast mass is detected through palpation in a physical examination. Imaging studies help assess the mammary gland to differentiate between gynecomastia and other conditions. Breast ultrasound is particularly effective at providing visual representation of breast tissue, distinguishing between fatty and glandular types, which supports precise diagnosis and informs subsequent treatment strategies.
Treatment Options for Adolescent Gynecomastia
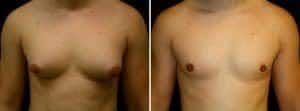
The range of treatment strategies for gynecomastia in adolescents depends on the condition’s intensity and its root causes. The issue often resolves naturally over several years, so a wait-and-see approach coupled with non-invasive treatments is appropriate for many young males. Studies show that breast enlargement of one or both breasts will resolve within 2 years., if not, it will become persistent.
Gynecomastia treated with medications, hormone therapy, or gynecomastia surgery may be necessary if the condition persists or is severe. Pharmacological interventions, such as hormone therapy or altering current medications, can also play a role in addressing gynecomastia by striving to equalize hormonal imbalances and curtail the development of breast enlargement.
If the condition is pronounced or resistant to other forms of intervention, male breast reduction surgery may be necessary. This procedure involves excising dense breast tissue and adipose tissues to create a chest profile that aligns more closely with typical male aesthetics. Understanding these alternatives equips individuals with vital insights needed for informed decision-making.
Monitoring and Non-Surgical Approaches
Watchful waiting is usually the initial strategy for dealing with gynecomastia, especially when there’s no identified underlying cause. It’s often sufficient to monitor the condition closely, as it typically subsides on its own within two years after appearing. Adopting lifestyle modifications like controlling weight may also contribute to diminishing signs of gynecomastia.
Alternative non-surgical methods, such as compression garments, can be effective in concealing the physical manifestations of gynecomastia and offering psychological comfort to individuals coping with this issue. Such tactics are particularly advantageous for those who prefer to steer clear of more aggressive medical interventions.
Medical Treatments
Treatment options for gynecomastia often involve hormone therapy or adjustments in existing medication, which can effectively manage the condition. Tamoxifen, known for its anti-estrogen properties, is commonly recommended, as it has proven successful in diminishing breast tissue. In certain cases, aromatase inhibitors such as anastrozole are also considered. Their success rate isn’t as clearly established.
Clomiphene citrate may be employed to address gynecomastia too—it functions both as a mild estrogen and a moderate anti-estrogen. The purpose of these treatments is to rebalance hormones and alleviate the signs of gynecomastia, so that surgical methods might not be necessary.
Surgical Treatment Solutions
For cases of gynecomastia that don’t respond to other treatments, surgical intervention may be considered. Liposuction and excision of one or both breasts are frequently employed to eliminate surplus glandular and adipose tissue. A common approach is the peri-areolar or Webster incision technique, where a cut is made around the bottom edge of the areola for tissue extraction.
Surgical treatment aims to improve cosmetic outcomes for individuals with gynecomastia. Alternatively, there’s the double incision method with free nipple grafting, designed for removal of additional skin and tissue to attain a chest contour that appears more masculine. Recuperation from surgery addressing gynecomastia spans four to six weeks, during which patients should curtail strenuous activities to ensure proper healing.
Psychological Impact and Support
The psychological toll of gynecomastia, marked by diminished self-worth and altered perception of body image, is significant. The emotional distress stems from both societal norms and personal discomfort.
Anxiety, depression, and a tendency to isolate socially are frequent mental health concerns connected to gynecomastia. Individuals may experience considerable unease and mortification even when the physical manifestation of the condition is relatively minor—this can lead to substantial losses in confidence and less engagement in social activities.
Accessing emotional assistance through therapeutic means or support networks can play a critical role in managing these psychological effects for those affected by gynecomastia. Psychosocial support is crucial for individuals dealing with the emotional distress caused by gynecomastia. Such avenues provide:
- Community belonging
- Exchange of similar experiences
- Directional counsel
- Sustained morale
With this type of support framework, persons dealing with gynecomastia may find it somewhat easier to deal with its associated challenges.
Counseling and Support Groups
Psychotherapy plays a crucial role in helping people handle the emotional distress caused by gynecomastia. It is frequently suggested for those undergoing treatment and recovery from gynecomastia as an essential component of their care.
For individuals grappling with the difficulties of gynecomastia, support groups can provide tremendous benefits. They foster a feeling of belonging and collective experience, offering both comfort on an emotional level and actionable guidance which can be instrumental in managing life with the condition. Peer support groups can provide emotional comfort and practical advice for individuals with gynecomastia.
Preventing Gynecomastia
To implement preventive measures against gynecomastia, it’s essential to:
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Consume a balanced diet
- Lead a healthy lifestyle overall
Such actions promote hormonal equilibrium and can diminish the chance of experiencing gynecomastia.
It is particularly crucial for adolescents to refrain from taking anabolic steroids or other substances designed to enhance athletic performance, as these agents are recognized causes of gynecomastia. They should also exercise caution in regards to androgen deprivation therapy, due to its potential role in inducing this condition. Minimizing alcohol consumption and steering clear of recreational drugs, such as marijuana, helps prevent gynecomastia.
By making prudent decisions regarding their lifestyle and staying aware of hazards that may lead to gynecomastia, adolescents can not only reduce their risk, but also improve their general health.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for hormonal health, particularly during puberty, when hormones are likely to fluctuate. Consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps sustain both hormonal equilibrium and general well-being. Maintaining nutritional balance is crucial for hormonal health.
Regular physical activity not only supports weight management, but also promotes balance within the endocrine system, which diminishes the likelihood of encountering conditions such as gynecomastia. Encouraging healthy practices early on can lead to enduring advantages for an individual’s overall health.
Avoiding Risk Factors
To avoid gynecomastia, one should steer clear of recreational drugs like marijuana, avoid substance abuse, and curtail alcohol consumption. Such substances can interfere with hormonal equilibrium, leading to an increase in breast tissue.
By understanding these risk contributors, adolescents can markedly diminish their likelihood of developing gynecomastia. The cornerstone for preventing this condition lies in education and heightened awareness about these factors.
Dr. Delgado- San Francisco is a top gynecomastia expert.

Internationally acclaimed for his proficiency in gynecomastia, Dr. Miguel Delgado is a board-certified plastic surgeon who assumes the role of medical director at Gynecomastia.org, which is a premier platform on this topic. His excellence in the field has been recognized with an accolade from San Francisco Magazine, naming him the top plastic surgeon in San Francisco.
Dr. Delgado’s surgical practice heavily emphasizes revision surgeries for those dissatisfied with their previous male breast reduction procedures. Patients worldwide seek his skill and commitment to correct issues arising from prior treatments related to gynecomastia. Individuals affected by this condition can experience substantial improvement in their treatment results when under the care of an authority like Dr. Delgado.
Summary
Adolescent boys going through puberty may find the experience of gynecomastia difficult, but a proper grasp of its origins, methods for diagnosis, and possible treatments can help effectively control this condition. The development of gynecomastia is predominantly due to hormonal imbalances, but can also be attributed to certain medications or substance abuse, as well as existing medical issues. Identifying the condition typically involves comprehensive physical assessments, blood testing and various imaging techniques.
When considering how to manage this health issue, strategies vary from observation and non-invasive practices to pharmacological interventions and surgery when necessary. Equally critical is addressing the emotional effects of gynecomastia. Support structures like counseling services and peer groups play an instrumental role here. Adopting healthy habits while steering clear of known risk factors serves as preventive steps that could lower one’s chances of developing gynecology.
Being well-educated about the matter, coupled with attaining suitable help, allows young individuals facing these challenges—and their families—to approach it with certainty and fortitude.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes gynecomastia during puberty?
During puberty, an imbalance in hormones can lead to gynecomastia. Additionally, certain medications and drugs, including anabolic steroids, can also cause this condition.
How is gynecomastia diagnosed?
Through physical exams, blood tests to measure hormone levels, and imaging techniques like ultrasound or mammography, gynecomastia can be diagnosed.
The identification of the condition is aided by assessing hormone concentrations via blood testing.
What are the treatment options for gynecomastia?
Options for managing gynecomastia range from watchful waiting to non-invasive methods, along with pharmaceutical interventions such as hormone therapy, and extend to surgical procedures in more extreme instances.
Seeking guidance from a medical expert is crucial in deciding the most appropriate treatment strategy.
Can gynecomastia resolve on its own?
Indeed, gynecomastia has the potential to subside independently, usually in a span of several months up to two years, without necessitating any form of treatment.
What can be done to prevent gynecomastia?
It is essential to uphold a healthy lifestyle, steer clear of anabolic steroids and recreational substances, and curtail the consumption of alcohol to deter the development of gynecomastia.
